Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Interpolation and Regriding#
Before proceeding with all the steps, first import some necessary libraries and packages
import easyclimate as ecl
import xarray as xr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import numpy as np
Interpolation from points to grid (European region only)#
Open sample surface pressure data for the European region
lat lon qff
0 43.8569 4.4064 1016.2
1 56.3265 -3.7273 995.1
2 55.7350 24.4170 1015.5
3 60.3000 -4.2000 997.8
4 57.8500 45.7667 1020.5
.. ... ... ...
867 38.8766 22.4360 1011.8
868 68.8493 28.2991 1018.2
869 39.0633 26.5983 1010.9
870 49.4464 2.1272 1009.8
871 61.3667 30.8833 1021.2
[872 rows x 3 columns]
easyclimate.interp.interp_spatial_barnes enables interpolation from site data to grid point data.
See also
Zürcher, B. K.: Fast approximate Barnes interpolation: illustrated by Python-Numba implementation fast-barnes-py v1.0, Geosci. Model Dev., 16, 1697–1711, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-16-1697-2023, 2023.
Plotting interpolated grid point data and corresponding station locations
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=0)})
ax.gridlines(draw_labels=["bottom", "left"], color="grey", alpha=0.5, linestyle="--")
ax.coastlines(edgecolor="black", linewidths=0.5)
ax.set_extent([-30, 15, 32, 75])
# Draw interpolation results
meshdata.plot.contourf(
ax=ax,
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
cbar_kwargs={"location": "bottom"},
cmap="RdBu_r",
levels=21,
)
# Draw observation stations
ax.scatter(data["lon"], data["lat"], s=1, c="r", transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
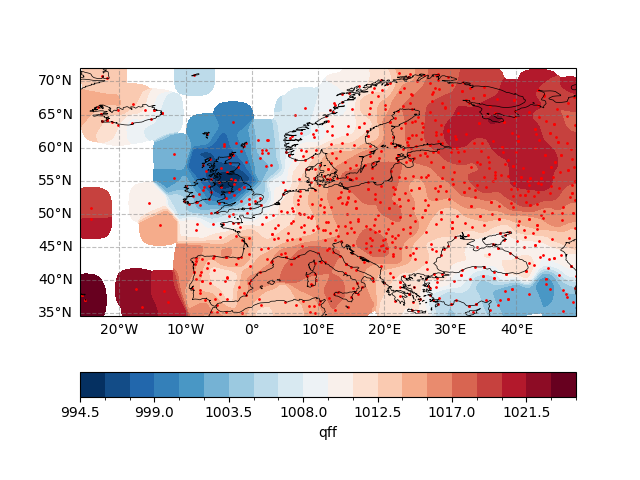
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x7fe72eabeb90>
Warning
The supported geographical domain and projection (as in the paper) is currently fixed to the European latitudes and Lambert conformal projection and cannot be freely chosen.
Regriding#
Reading example raw grid data
Define the target grid (only for latitude/longitude and regular grids)
target_grid = xr.DataArray(
dims=("lat", "lon"),
coords={
"lat": np.arange(-89, 89, 6) + 1 / 1.0,
"lon": np.arange(-180, 180, 6) + 1 / 1.0,
},
)
easyclimate.interp.interp_mesh2mesh performs a regridding operation.
See also
regriding_data = ecl.interp.interp_mesh2mesh(u_data, target_grid)
regriding_data
/home/runner/work/easyclimate/easyclimate/src/easyclimate/interp/mesh2mesh.py:94: UserWarning: It seems that the input data longitude range is from -180° to 180°. Currently automatically converted to it from 0° to 360°.
warnings.warn(
Plotting differences before and after interpolation
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
u_data.sel(level=500).isel(time=0).plot(ax=ax[0])
ax[0].set_title("Before", size=20)
regriding_data.sel(level=500).isel(time=0).plot(ax=ax[1])
ax[1].set_title("After", size=20)
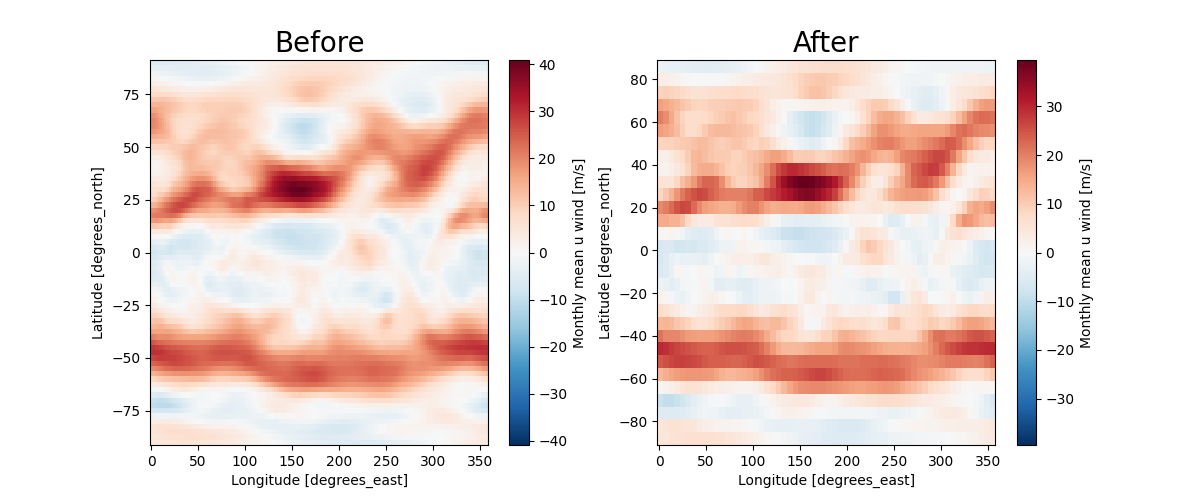
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'After')
Interpolation from model layers to altitude layers#
Suppose the following data are available
uwnd_data = xr.DataArray(
np.array([ -15.080393 , -10.749071 , -4.7920494, -2.3813725, -1.4152431,
-0.6465206, -7.8181705, -14.718096 , -14.65539 , -14.948015 ,
-13.705519 , -11.443476 , -8.865583 , -7.9528713, -8.329103 ,
-7.2445316, -6.7150173, -5.5189686, -4.139448 , -3.2731838,
-2.2931194, -1.0041752, -1.8983078, -2.3674374, -2.8203106,
-3.2940865, -3.526329 , -3.8654022, -4.164995 , -4.2834396,
-4.2950516, -4.3438225, -4.3716908, -4.7688255, -4.6155453,
-4.5528393, -4.4831676, -4.385626 , -4.2950516, -4.0953217]),
dims=("model_level",),
coords={
"model_level": np.array([ 36, 44, 51, 56, 60, 63, 67, 70, 73, 75, 78, 81, 83,
85, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 100, 102, 104, 105, 107, 109,
111, 113, 115, 117, 119, 122, 124, 126, 129, 131, 133, 135, 136,
137])
},
)
p_data = xr.DataArray(
np.array([ 2081.4756, 3917.6995, 6162.6455, 8171.3506, 10112.652 ,
11811.783 , 14447.391 , 16734.607 , 19317.787 , 21218.21 ,
24357.875 , 27871.277 , 30436.492 , 33191.027 , 37698.96 ,
40969.438 , 44463.73 , 48191.92 , 52151.29 , 56291.098 ,
60525.63 , 64770.367 , 68943.69 , 70979.66 , 74908.17 ,
78599.67 , 82012.95 , 85122.69 , 87918.29 , 90401.77 ,
92584.94 , 95338.72 , 96862.08 , 98165.305 , 99763.38 ,
100626.21 , 101352.69 , 101962.28 , 102228.875 , 102483.055 ]),
dims=("model_level",),
coords={
"model_level": np.array([ 36, 44, 51, 56, 60, 63, 67, 70, 73, 75, 78, 81, 83,
85, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 100, 102, 104, 105, 107, 109,
111, 113, 115, 117, 119, 122, 124, 126, 129, 131, 133, 135, 136,
137])
},
)
Now we interpolate the data located on the mode plane to the isobaric plane. Note that the units of the given isobaric surface are consistent with pressure_data.
Simply calibrate the interpolation effect.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(p_data, uwnd_data, label="Original")
ax.plot(result.plev, result.data, "o", label="Interpolated")
ax.invert_xaxis()
ax.set_xlabel("Pressure [Pa]")
ax.set_ylabel("Zonal Wind [m/s]")
plt.legend()
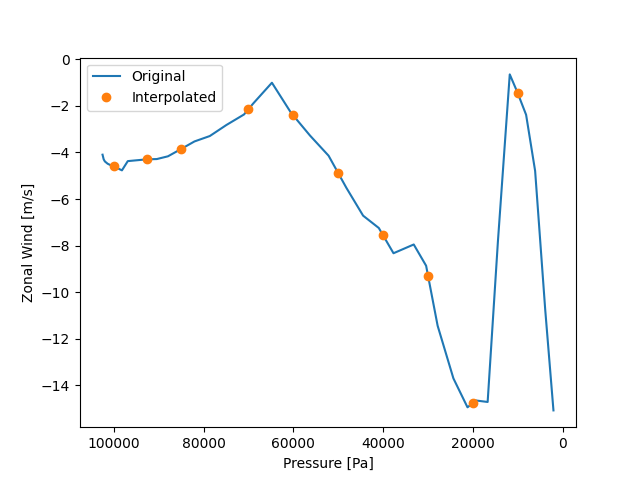
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7fe72eeda740>
Interpolation from pressure layers to altitude layers#
Suppose the following data are available
z_data = xr.DataArray(
np.array([ 214.19354, 841.6774 , 1516.871 , 3055.7097 , 4260.5806 ,
5651.4194 , 7288.032 , 9288.193 , 10501.097 , 11946.71 ,
13762.322 , 16233.451 , 18370.902 , 20415.227 , 23619.033 ,
26214.322 , 30731.807 ]),
dims=("level"),
coords={
"level": np.array([ 1000., 925., 850., 700., 600., 500., 400., 300., 250.,
200., 150., 100., 70., 50., 30., 20., 10.])
},
)
uwnd_data = xr.DataArray(
np.array([ -2.3200073, -3.5700073, -2.5800018, 8.080002 , 14.059998 ,
22.119995 , 33.819992 , 49.339996 , 57.86 , 64.009995 ,
62.940002 , 49.809998 , 31.160004 , 16.59999 , 10.300003 ,
10.459991 , 9.880005 ]),
dims=("level"),
coords={
"level": np.array([ 1000., 925., 850., 700., 600., 500., 400., 300., 250.,
200., 150., 100., 70., 50., 30., 20., 10.])
},
)
Then we need to interpolate the zonal wind data (located on the isobaric surface) to the altitude layers.
target_heights = np.linspace(0, 10000, 101)
result = ecl.interp.interp1d_vertical_pressure2altitude(
z_data=z_data,
variable_data=uwnd_data,
target_heights=target_heights,
vertical_input_dim="level",
vertical_output_dim="altitude",
)
result
Now we can check the interpolation results.
plt.plot(z_data[:9], uwnd_data[:9], "o", label="Original")
plt.plot(result.altitude, result.data, label="Interpolated")
plt.xlabel("Altitude [m]")
plt.ylabel("Zonal Wind [m/s]")
plt.legend()
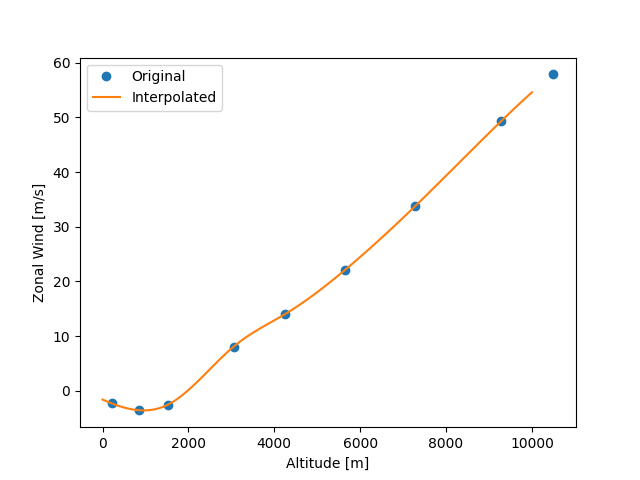
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7fe72ea0b2e0>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 12.360 seconds)